Literature exploration: in-memory analytics tutorial¶
In this example we illustrate how network analytics can be used for literature exploration. The source notebook can be found here.
The input dataset contains occurrences of different terms in paragraphs of scientific articles previously extracted by means of a Named Entity Recognition (NER) model. This dataset is transformed into three co-occurrence networks: representing paper- and paragraph-level co-occurrence relation between terms. The term relations in the above-mentioned networks are quantified using mutual-information-based scores (pointwise mutual information and its normalized version).
The networks are further analysed using classical tools from complex networks: we find various centrality measures characterizing the importance of extracted terms, we detect term communities representing denesely connected clusters of terms and finally we illustrate how the algorithms for finding shortest paths and minimum spanning trees can be used to perform guided search in networks.
import networkx as nx
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from bluegraph.core import (PandasPGFrame,
pretty_print_paths,
pretty_print_tripaths,
graph_elements_from_paths)
from bluegraph.preprocess.generators import CooccurrenceGenerator
from bluegraph.backends.graph_tool import (GTMetricProcessor,
GTPathFinder,
GTGraphProcessor,
GTCommunityDetector)
from bluegraph.backends.graph_tool import graph_tool_to_pgframe
from bluegraph.backends.networkx import NXCommunityDetector, NXPathFinder
from bluegraph.backends.stellargraph import StellarGraphNodeEmbedder
Entity-occurrence property graph¶
In this section we will create a property graph whose nodes are papers and extracted named entities, and whose edges connect entities to the papers they occur in.
The input data is given by occurrences of different entities in specific paragraphs of scientific articles.
mentions = pd.read_csv("../data/literature_NER_example.csv")
mentions.sample(5)
| entity | occurrence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1510 | viral | 214924:The Protective Role Of Angiotensin-Conv... |
| 720 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4 | 184360:Cardiovascular Effects Of Sdpp4 Upregul... |
| 1019 | insulin | 214924:The Interplay Between Covid-19 And Ampk... |
| 556 | diabetes mellitus | 184360:Mechanisms Of Sars-Cov-2 Entry Into Hos... |
| 540 | diabetes mellitus | 214924:Introduction:7 |
Every paragraph is identified using the format
<paper_id>:<section_id>:<paragraph_id>. From this data we will
extract occurrences in distinct papers/paragraphs as follows:
# Extract unique paper/seciton/paragraph identifiers
mentions["paper"] = mentions["occurrence"].apply(
lambda x: x.split(":")[0])
mentions = mentions.rename(columns={"occurrence": "paragraph"})
mentions.sample(5)
| entity | paragraph | paper | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 154 | blood | 214728:Cap Community-Acquired Pneumonia Covid-... | 214728 |
| 833 | glycosylated hemoglobin measurement | 184360:Gliptins ::: Therapeutic Potential Of T... | 184360 |
| 1506 | viral | 214924:The Interplay Between Covid-19 And Ampk... | 214924 |
| 936 | hypertension | 211125:Introduction:5 | 211125 |
| 828 | glyburide | 160564:Data Extraction And Study Quality ::: M... | 160564 |
We, first, create an empty property graph object.
graph = PandasPGFrame()
Then we add nodes for unique entities and papers
entity_nodes = mentions["entity"].unique()
graph.add_nodes(entity_nodes)
graph.add_node_types({n: "Entity" for n in entity_nodes})
paper_nodes = mentions["paper"].unique()
graph.add_nodes(paper_nodes)
graph.add_node_types({n: "Paper" for n in paper_nodes})
graph.nodes(raw_frame=True)
| @type | |
|---|---|
| @id | |
| ace inhibitor | Entity |
| acetaminophen | Entity |
| acute lung injury | Entity |
| acute respiratory distress syndrome | Entity |
| adenosine | Entity |
| ... | ... |
| 78884 | Paper |
| 35198 | Paper |
| 139943 | Paper |
| 172581 | Paper |
| 102473 | Paper |
177 rows × 1 columns
We now add edges from entities to the papers they occur in storing paragraphs as edge properties.
occurrence_edges = mentions.groupby(by=["entity", "paper"]).aggregate(set)
occurrence_edges
| paragraph | ||
|---|---|---|
| entity | paper | |
| ace inhibitor | 184360 | {184360:Conclusion:62, 184360:Combined Therape... |
| 197804 | {197804:Caption:71, 197804:Caption:72, 197804:... | |
| acetaminophen | 179426 | {179426:Blood Glucose Monitoring ::: Special A... |
| 197804 | {197804:Discussion:51, 197804:Discussion:52, 1... | |
| acute lung injury | 179426 | {179426:Role Of Ace/Arbs ::: Special Aspects O... |
| ... | ... | ... |
| virus | 184360 | {184360:Gliptins ::: Therapeutic Potential Of ... |
| 197804 | {197804:Discussion:44, 197804:Introduction:2} | |
| 211125 | {211125:Discussion:25} | |
| 211373 | {211373:Introduction:5, 211373:Introduction:6,... | |
| 214924 | {214924:Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expres... |
551 rows × 1 columns
graph.add_edges(occurrence_edges.index)
graph.add_edge_types({e: "OccursIn" for e in occurrence_edges.index})
occurrence_edges.index = occurrence_edges.index.rename(["@source_id", "@target_id"])
graph.add_edge_properties(occurrence_edges["paragraph"])
graph.edges(raw_frame=True)
| @type | paragraph | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | ||
| ace inhibitor | 184360 | OccursIn | {184360:Conclusion:62, 184360:Combined Therape... |
| 197804 | OccursIn | {197804:Caption:71, 197804:Caption:72, 197804:... | |
| acetaminophen | 179426 | OccursIn | {179426:Blood Glucose Monitoring ::: Special A... |
| 197804 | OccursIn | {197804:Discussion:51, 197804:Discussion:52, 1... | |
| acute lung injury | 179426 | OccursIn | {179426:Role Of Ace/Arbs ::: Special Aspects O... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| virus | 184360 | OccursIn | {184360:Gliptins ::: Therapeutic Potential Of ... |
| 197804 | OccursIn | {197804:Discussion:44, 197804:Introduction:2} | |
| 211125 | OccursIn | {211125:Discussion:25} | |
| 211373 | OccursIn | {211373:Introduction:5, 211373:Introduction:6,... | |
| 214924 | OccursIn | {214924:Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expres... |
551 rows × 2 columns
Entity co-occurrence graphs¶
We will generate co-occurrence graphs for different occurrence factors (paper/paragraph), i.e. an edge between a pair of entities is added if they co-occur in the same paper or paragraph.
NB: Read more about statistics computed during the co-occurrence analysis (positive pointwise mutual information (PPMI) and normalized pointwise mutual information (NPMI)) here.
Paper-based co-occurrence¶
We first generate co-occurrence network from edges of type OccursIn
linking entities and papers.
gen = CooccurrenceGenerator(graph)
paper_cooccurrence_edges = gen.generate_from_edges(
"OccursIn", compute_statistics=["frequency", "ppmi", "npmi"])
Examining 12246 pairs of terms for co-occurrence...
paper_cooccurrence_edges["@type"] = "CoOccursWith"
paper_cooccurrence_edges
| common_factors | frequency | ppmi | npmi | @type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | |||||
| ace inhibitor | acetaminophen | {197804} | 1 | 2.321928 | 0.537244 | CoOccursWith |
| acute lung injury | {197804, 184360} | 2 | 2.321928 | 0.698970 | CoOccursWith | |
| acute respiratory distress syndrome | {197804, 184360} | 2 | 1.736966 | 0.522879 | CoOccursWith | |
| adenosine | {184360} | 1 | 2.321928 | 0.537244 | CoOccursWith | |
| adipose tissue | {197804, 184360} | 2 | 2.736966 | 0.823909 | CoOccursWith | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| viral | viral infection | {184360, 211125, 214924, 211373} | 4 | 2.000000 | 0.861353 | CoOccursWith |
| virus | {214924, 184360, 211373, 211125, 179426} | 5 | 1.514573 | 0.757287 | CoOccursWith | |
| viral entry | viral infection | {214924} | 1 | 1.321928 | 0.305865 | CoOccursWith |
| virus | {179426, 214924} | 2 | 1.514573 | 0.455932 | CoOccursWith | |
| viral infection | virus | {184360, 211125, 214924, 211373} | 4 | 1.514573 | 0.652291 | CoOccursWith |
9748 rows × 5 columns
From the generated edges we remove the ones with zero NPMI scores.
paper_cooccurrence_edges = paper_cooccurrence_edges[paper_cooccurrence_edges["npmi"] != 0]
entity_nodes = graph.nodes_of_type("Entity").copy()
paper_frequency = mentions.groupby("entity").aggregate(set)["paper"].apply(len)
paper_frequency.name = "paper_frequency"
entity_nodes["paper_frequency"] = paper_frequency
We create a new property graph object from generated edges and entity nodes as follows:
paper_network = PandasPGFrame.from_frames(
nodes=entity_nodes,
edges=paper_cooccurrence_edges,
node_prop_types={
"paper_frequency": "numeric",
"paragraph_frequency": "numeric"
},
edge_prop_types={
"frequency": "numeric",
"ppmi": "numeric",
"npmi": "numeric"
})
paper_network.edges(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| common_factors | frequency | ppmi | npmi | @type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | |||||
| cough | pneumonia | {211125, 197804, 214924, 184360} | 4 | 1.321928 | 0.569323 | CoOccursWith |
| cytokine | oxygen | {211125} | 1 | 1.736966 | 0.401896 | CoOccursWith |
| chronic disease | vildagliptin | {179426} | 1 | 2.321928 | 0.537244 | CoOccursWith |
| insulin | receptor binding | {197804} | 1 | 0.514573 | 0.119061 | CoOccursWith |
| hyperglycemia | tumor necrosis factor | {211125, 214924, 184360} | 3 | 1.321928 | 0.482990 | CoOccursWith |
paper_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| @type | paper_frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| @id | ||
| myalgia | Entity | 2 |
| prognosis | Entity | 2 |
| apoptosis | Entity | 2 |
| thrombophilia | Entity | 3 |
| septicemia | Entity | 2 |
Paragraph-based co-occurrence¶
We perform similar operation for paragraph-level co-occurrence. In order
to use another co-occurrence factor, we will define the following
‘factor_aggregator’ function (aggregate_paragraph) that takes a
collection of sets of paragraphs and merges them into the same set. This
aggregator will be used to collect sets of common paragraphs of
OccursIn edges pointing from a pair of entities to the same paper.
def aggregate_paragraphs(data):
return set(sum(data["paragraph"].apply(list), []))
%%time
paragraph_cooccurrence_edges = gen.generate_from_edges(
"OccursIn",
factor_aggregator=aggregate_paragraphs,
compute_statistics=["frequency", "ppmi", "npmi"],
parallelize=True, cores=8)
Computing total factor instances...
Examining 12246 pairs of terms for co-occurrence...
CPU times: user 78.8 ms, sys: 62.1 ms, total: 141 ms
Wall time: 5.39 s
paragraph_cooccurrence_edges["@type"] = "CoOccursWith"
paragraph_cooccurrence_edges.sample(5)
| common_factors | frequency | ppmi | npmi | @type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | |||||
| dpp4i | glycosylated hemoglobin measurement | {184360:Gliptins ::: Therapeutic Potential Of ... | 1 | 2.736966 | 0.336680 | CoOccursWith |
| h1n1 | virus | {214924:The Interplay Between Covid-19 And Amp... | 1 | 2.669851 | 0.328424 | CoOccursWith |
| interleukin-6 | middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus | {214924:Diabetes Mellitus And Covid-19: In The... | 2 | 0.415037 | 0.058216 | CoOccursWith |
| insulin resistance | t-lymphocyte | {184360:Cardiovascular Effects Of Sdpp4 Upregu... | 1 | 3.000000 | 0.369036 | CoOccursWith |
| dna replication | middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus | {214924:The Interplay Between Covid-19 And Amp... | 2 | 2.152003 | 0.301854 | CoOccursWith |
From the generated edges we remove the ones with zero NPMI scores.
paragraph_cooccurrence_edges = paragraph_cooccurrence_edges[paragraph_cooccurrence_edges["npmi"] != 0]
paragraph_network = PandasPGFrame.from_frames(
nodes=entity_nodes,
edges=paragraph_cooccurrence_edges,
node_prop_types={
"paper_frequency": "numeric",
},
edge_prop_types={
"frequency": "numeric",
"ppmi": "numeric",
"npmi": "numeric"
})
Faster paragraph-based co-occurrence¶
Alternatively, to generate paragraph-level co-occurrence network, we can assign sets of paragraphs where entities occur as properties of their respective nodes (as follows).
paragraph_prop = pd.DataFrame({"paragraphs": mentions.groupby("entity").aggregate(set)["paragraph"]})
graph.add_node_properties(paragraph_prop, prop_type="category")
graph.nodes(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| @type | paragraphs | |
|---|---|---|
| @id | ||
| islet of langerhans | Entity | {179426:Effect Of Sars Cov-2 On Blood Glucose ... |
| multi-organ dysfunction | Entity | {179426:Morbidity And Mortality In Diabetic Co... |
| angiotensin ii receptor antagonist | Entity | {214924:Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Expres... |
| m protein | Entity | {184360:Cardiovascular Effects Of Sdpp4 Upregu... |
| insulin infusion | Entity | {179426:Glycemic Control ::: Special Aspects O... |
And then use the generate_from_nodes method of
CooccurrenceGenerator in order to generate co-occurrence edges for
nodes whose paragraphs property has a non-empty intersection.
%%time
generator = CooccurrenceGenerator(graph)
paragraph_cooccurrence_edges = generator.generate_from_nodes(
"paragraphs", total_factor_instances=len(mentions.paragraph.unique()),
compute_statistics=["frequency", "npmi"],
parallelize=True, cores=8)
Examining 15576 pairs of terms for co-occurrence...
CPU times: user 101 ms, sys: 69.7 ms, total: 170 ms
Wall time: 1.37 s
Additional co-occurrence measures: NPMI-based distance¶
For both paper- and paragraph-based networks we will compute a mutual-information-based distance as follows: \(D = \frac{1}{NPMI}\).
import math
def compute_distance(x):
return 1 / x if x > 0 else math.inf
npmi_distance = paper_network.edges(raw_frame=True)["npmi"].apply(compute_distance)
npmi_distance.name = "distance_npmi"
paper_network.add_edge_properties(npmi_distance, "numeric")
paper_network.edges(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| common_factors | frequency | ppmi | npmi | @type | distance_npmi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | ||||||
| inflammation | tumor necrosis factor | {211125, 214924, 184360} | 3 | 1.736966 | 0.634632 | CoOccursWith | 1.575717 |
| fever | islet of langerhans | {211125} | 1 | 1.736966 | 0.401896 | CoOccursWith | 2.488206 |
| acute respiratory distress syndrome | immune response process | {214924, 184360} | 2 | 1.152003 | 0.346787 | CoOccursWith | 2.883610 |
| angiotensin ii receptor antagonist | influenza | {179426, 214924, 184360} | 3 | 2.736966 | 1.000000 | CoOccursWith | 1.000000 |
| lower respiratory tract infection | lymphopenia | {211125, 214924} | 2 | 2.152003 | 0.647817 | CoOccursWith | 1.543645 |
npmi_distance = paragraph_network.edges(raw_frame=True)["npmi"].apply(compute_distance)
npmi_distance.name = "distance_npmi"
paragraph_network.add_edge_properties(npmi_distance, "numeric")
paper_network.edges(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| common_factors | frequency | ppmi | npmi | @type | distance_npmi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @source_id | @target_id | ||||||
| influenza | viral entry | {179426, 214924} | 2 | 2.736966 | 0.823909 | CoOccursWith | 1.213727 |
| blood vessel | viral entry | {214924} | 1 | 2.321928 | 0.537244 | CoOccursWith | 1.861353 |
| hyperglycemia | pneumonia | {214924, 184360, 214728, 211125, 179426} | 5 | 0.643856 | 0.321928 | CoOccursWith | 3.106284 |
| death | sitagliptin | {179426, 184360} | 2 | 0.567041 | 0.170696 | CoOccursWith | 5.858360 |
| adipose tissue | fatigue | {214924} | 1 | 1.736966 | 0.401896 | CoOccursWith | 2.488206 |
Nearest neighours by co-occurrence scores¶
To illustrate the importance of computing mutual-information-based scores over raw frequencies consider the following example, where we would like to estimate top closest (most related) neighbors to a specific term.
To do so, we will use the paragraph-based network and the raw
co-occurrence frequency as the weight of our co-occurrence relation. The
top_neighbors method of the PathFinder interface provided by the
BlueGraph allows us to search for top neighbors with the highest edge
weight. In this example, we use graph_tool-based GTPathFinder
interface.
paragraph_path_finder = GTPathFinder(paragraph_network, directed=False)
Observe in the following cell that the path finder interface generated a backend-specific graph object.
paragraph_path_finder.graph
<Graph object, undirected, with 157 vertices and 2479 edges at 0x7fc6ae5b76d8>
paragraph_path_finder.top_neighbors("glucose", 10, weight="frequency")
{'diabetes mellitus': 29.0,
'blood': 18.0,
'insulin': 11.0,
'death': 9.0,
'hyperglycemia': 8.0,
'coronavirus': 8.0,
'infectious disorder': 6.0,
'inflammation': 6.0,
'sars coronavirus': 6.0,
'interleukin-6': 5.0}
paragraph_path_finder.top_neighbors("lung", 10, weight="frequency")
{'covid-19': 24.0,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme 2': 16.0,
'sars-cov-2': 13.0,
'acute lung injury': 12.0,
'pulmonary': 10.0,
'sars coronavirus': 10.0,
'viral': 9.0,
'human': 9.0,
'mouse': 7.0,
'inflammation': 6.0}
We observe that ‘glucose’ and ‘lung’ share a lot of the closest neighbors by raw frequency. If we look into the list of top 10 entities by paragraph frequency in the entire corpus and we notice that ‘glucose’ and ‘blood’ co-occur the most with the terms that are simply the most frequent in our corpus, such as ‘covid-19’ and ‘diabetes mellitus’.
(Closest inspection of the distribution of weighted node degrees suggests that the network contains hubs, nodes with significantly high-degree connectivity to other nodes.)
paragraph_network._nodes
| @type | paper_frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| @id | ||
| ace inhibitor | Entity | 2 |
| acetaminophen | Entity | 2 |
| acute lung injury | Entity | 4 |
| acute respiratory distress syndrome | Entity | 6 |
| adenosine | Entity | 2 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| vildagliptin | Entity | 2 |
| viral | Entity | 5 |
| viral entry | Entity | 2 |
| viral infection | Entity | 4 |
| virus | Entity | 7 |
157 rows × 2 columns
paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).nlargest(10, columns=["paper_frequency"])
| @type | paper_frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| @id | ||
| covid-19 | Entity | 20 |
| diabetes mellitus | Entity | 19 |
| coronavirus | Entity | 16 |
| glucose | Entity | 13 |
| death | Entity | 9 |
| glyburide | Entity | 9 |
| infectious disorder | Entity | 9 |
| blood | Entity | 8 |
| hyperglycemia | Entity | 8 |
| pneumonia | Entity | 8 |
To account for the presence of such hubs, we use the mutual-information-based scores presented above. They ‘balance’ the influence of the highly connected hub nodes such as ‘covid-19’ and ‘diabetes mellitus’ in our example.
paragraph_path_finder.top_neighbors("glucose", 10, weight="npmi")
{'blood': 0.5133209650995287,
'glucose metabolism disorder': 0.43558951200762297,
'insulin': 0.41957609533629175,
'thrombophilia': 0.4079646453270325,
'insulin infusion': 0.3744908698338857,
'leukopenia': 0.3744908698338857,
'millimole per liter': 0.3744908698338857,
'troponin t, cardiac muscle': 0.3744908698338857,
'bals r': 0.3744908698338857,
'hyperglycemia': 0.3255525953220345}
paragraph_path_finder.top_neighbors("lung", 10, weight="npmi")
{'acute lung injury': 0.731006557092012,
'pulmonary': 0.6362945400636919,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme 2': 0.4757184436640079,
'receptor binding': 0.46595542454855043,
'viral infection': 0.4465392749200213,
'animal': 0.4465392749200213,
'mouse': 0.4362945258726772,
'angiotensin-1': 0.4259996541516483,
'viral': 0.4233482775367079,
'human': 0.4098154380746763}
Graph metrics and centrality measures¶
BlueGraph provides the MetricProcessor interface for computing
various graph statistics. As in the previous example, we will use
graph_tool-based GTMetricProcessor interface.
paper_metrics = GTMetricProcessor(paper_network, directed=False)
paragraph_metrics = GTMetricProcessor(paragraph_network, directed=False)
Graph density¶
Density of a graph is quantified by the proportion of all possible edges (\(n(n-1) / 2\) for the undirected graph with \(n\) nodes) that are realized.
print("Density of the paper-based network: ", paper_metrics.density())
print("Density of the paragraph-based network: ", paragraph_metrics.density())
Density of the paper-based network: 0.7769884043769394
Density of the paragraph-based network: 0.20243344765637758
The results above show that in the paper, section and paragraph network repsectively 80%, 42% and 22% of all possible term pairs co-occur at least once.
Node centrality (importance) measures¶
In this example we will compute the Degree and PageRank centralities
only for the raw frequency, and the Betweenness centrality for the
mutual-information-based scores. We will use methods provided by the
MetricProcessor interface in the write mode, i.e. computed metrics
will be written as node properties of the underlying graph object.
Degree centrality is given by the sum of weights of all incident edges of the given node and characterizes the importance of the node in the network in terms of its connectivity to other nodes (high degree = high connectivity).
paragraph_metrics.degree_centrality("frequency", write=True, write_property="degree")
PageRank centrality is another measure that estimated the importance of the given node in the network. Roughly speaking it can be interpreted as the probablity that having landed on a random node in the network we will jump to the given node (here the edge weights are taken into account”).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PageRank
paragraph_metrics.pagerank_centrality("frequency", write=True, write_property="pagerank")
We then compute the betweenness centrality based on the NPMI distances.
Betweenness centrality is a node importance measure that estimates how often a shortest path between a pair of nodes will pass through the given node.
paragraph_metrics.betweenness_centrality("distance_npmi", write=True, write_property="betweenness")
We can inspect the underlying graph object and observe the newly added properties:
paragraph_metrics.graph.vp.keys()
['@id', '@type', 'paper_frequency', 'degree', 'pagerank', 'betweenness']
Now, we will export this backend-specific graph object into a
PGFrame.
new_paragraph_network = paragraph_metrics.get_pgframe()
new_paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| @type | paper_frequency | degree | pagerank | betweenness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @id | |||||
| iv | Entity | 2.0 | 4.0 | 0.001286 | 0.000000 |
| chemokine | Entity | 3.0 | 43.0 | 0.004657 | 0.026730 |
| death | Entity | 9.0 | 194.0 | 0.015881 | 0.004632 |
| lymphopenia | Entity | 3.0 | 55.0 | 0.005415 | 0.038916 |
| bradykinin | Entity | 2.0 | 18.0 | 0.002771 | 0.004274 |
print("Top 10 nodes by degree")
for n in new_paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).nlargest(10, columns=["degree"]).index:
print("\t", n)
Top 10 nodes by degree
covid-19
diabetes mellitus
sars-cov-2
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
lung
coronavirus
dipeptidyl peptidase 4
glucose
sars coronavirus
interleukin-6
print("Top 10 nodes by PageRank")
for n in new_paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).nlargest(10, columns=["pagerank"]).index:
print("\t", n)
Top 10 nodes by PageRank
covid-19
diabetes mellitus
sars-cov-2
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
lung
dipeptidyl peptidase 4
glucose
coronavirus
sars coronavirus
interleukin-6
print("Top 10 nodes by betweenness")
for n in new_paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).nlargest(10, columns=["betweenness"]).index:
print("\t", n)
Top 10 nodes by betweenness
lymphopenia
pulmonary
glucose metabolism disorder
t-lymphocyte
cough
chemokine
d-dimer measurement
kidney
interleukin-19
ibuprofen
Compute multiple metrics in one go¶
Alternatively, we can compute all the metrics in one go. To do so, we need to specify edge attributes used for computing different metrics (if an empty list is specified as a weight list for a metric, computation of this metric is not performed).
We select the paragraph-based network and re-compute all some of the previously illustrated metrics as follows:
result_metrics = paragraph_metrics.compute_all_node_metrics(
degree_weights=["frequency"],
pagerank_weights=["frequency"],
betweenness_weights=["distance_npmi"])
result_metrics
{'degree': {'frequency': {'ace inhibitor': 39.0,
'acetaminophen': 5.0,
'acute lung injury': 128.0,
'acute respiratory distress syndrome': 139.0,
'adenosine': 22.0,
'adipose tissue': 27.0,
'angioedema': 20.0,
'angiotensin ii receptor antagonist': 85.0,
'angiotensin-1': 70.0,
'angiotensin-2': 18.0,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme': 13.0,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme 2': 329.0,
'animal': 47.0,
'apoptosis': 18.0,
'bals r': 6.0,
'basal': 34.0,
'blood': 115.0,
'blood vessel': 28.0,
'bradykinin': 18.0,
'c-c motif chemokine 1': 47.0,
'c-reactive protein': 31.0,
'cardiac failure': 17.0,
'cardiovascular disorder': 107.0,
'cardiovascular system': 115.0,
'cd44 antigen': 46.0,
'cellular secretion': 47.0,
'cerebrovascular': 18.0,
'chemokine': 43.0,
'chest pain': 21.0,
'chloroquine': 7.0,
'chronic disease': 12.0,
'chronic kidney disease': 18.0,
'comorbidity': 19.0,
'confounding factors': 26.0,
'coronaviridae': 54.0,
'coronavirus': 231.0,
'cough': 51.0,
'covid-19': 701.0,
'cytokine': 141.0,
'd-dimer measurement': 87.0,
'death': 194.0,
'degradation': 24.0,
'diabetes mellitus': 489.0,
'diabetic ketoacidosis': 46.0,
'diarrhea, ctcae': 35.0,
'dipeptidyl peptidase 4': 217.0,
'dna replication': 67.0,
'dpp4i': 92.0,
'dyspnea': 23.0,
'extracellular matrix': 14.0,
'fatigue': 23.0,
'fever': 40.0,
'glucose': 215.0,
'glucose metabolism disorder': 56.0,
'glyburide': 151.0,
'glycosylated hemoglobin measurement': 27.0,
'growth factor': 22.0,
'h1n1': 16.0,
'hcp': 25.0,
'headache': 24.0,
'heart': 107.0,
'heart failure': 17.0,
'high sensitivity c-reactive protein measurement': 52.0,
'hiv entry inhibitor': 59.0,
'hmg-coa reductase inhibitor': 18.0,
'host cell': 57.0,
'human': 169.0,
'human dpp4': 22.0,
'human immunodeficiency virus': 39.0,
'human kidney organoids': 17.0,
'humoral immunity': 19.0,
'hyperglycemia': 110.0,
'hypertension': 159.0,
'hypoxia': 15.0,
'ibuprofen': 23.0,
'immune cell': 27.0,
'immune response process': 34.0,
'infectious disorder': 194.0,
'inflammation': 154.0,
'influenza': 27.0,
'insulin': 100.0,
'insulin infusion': 13.0,
'insulin resistance': 65.0,
'interleukin': 18.0,
'interleukin 1 beta measurement': 78.0,
'interleukin-19': 56.0,
'interleukin-6': 209.0,
'interleukin-8': 35.0,
'islet of langerhans': 18.0,
'iv': 4.0,
'janus bifrons': 4.0,
'kidney': 89.0,
'leucopenia': 18.0,
'leukopenia': 26.0,
'liver': 42.0,
'lower respiratory tract infection': 43.0,
'lung': 259.0,
'lymphocyte': 50.0,
'lymphopenia': 55.0,
'm protein': 11.0,
'macrophage': 40.0,
'mellitus': 2.0,
'metformin': 39.0,
'middle east respiratory syndrome': 67.0,
'middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus': 171.0,
'millimole per liter': 16.0,
'molecule': 20.0,
'mouse': 140.0,
'multi-organ dysfunction': 23.0,
'muscle': 13.0,
'myalgia': 9.0,
'myocardium': 17.0,
'neoplasm': 26.0,
'nephropathy': 12.0,
'neutrophil': 66.0,
'obesity': 92.0,
'oral cavity': 57.0,
'organ': 24.0,
'oxygen': 13.0,
'person': 48.0,
'plasma': 57.0,
'plasmid': 21.0,
'pneumonia': 116.0,
'prognosis': 4.0,
'proliferation': 75.0,
'pulmonary': 137.0,
'rbd': 20.0,
'receptor binding': 12.0,
'renal': 35.0,
'respiratory failure': 23.0,
'respiratory system': 39.0,
'sars coronavirus': 213.0,
'sars-cov-2': 406.0,
'saxagliptin': 48.0,
'septicemia': 6.0,
'serum': 29.0,
'serum ferritin': 59.0,
'severe acute respiratory syndrome': 30.0,
'shortness of breath visual analogue scale': 18.0,
'sitagliptin': 103.0,
'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent': 27.0,
'survival': 34.0,
't-lymphocyte': 56.0,
'therapeutic corticosteroid': 28.0,
'thrombophilia': 39.0,
'tissue': 32.0,
'transmembrane protein': 22.0,
'troponin t, cardiac muscle': 26.0,
'tumor necrosis factor': 56.0,
'tzd': 26.0,
'vaccine': 33.0,
'vascular': 110.0,
'vildagliptin': 55.0,
'viral': 203.0,
'viral entry': 58.0,
'viral infection': 54.0,
'virus': 199.0}},
'pagerank': {'frequency': {'ace inhibitor': 0.004042530805234559,
'acetaminophen': 0.001438112847217684,
'acute lung injury': 0.010586985714212894,
'acute respiratory distress syndrome': 0.011867704712126654,
'adenosine': 0.0026917760651910213,
'adipose tissue': 0.003050180074112491,
'angioedema': 0.002756829710592291,
'angiotensin ii receptor antagonist': 0.00746809358002035,
'angiotensin-1': 0.006245821418420198,
'angiotensin-2': 0.002470853065990793,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme': 0.0021517440285987646,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme 2': 0.026787609075385067,
'animal': 0.004592419992089224,
'apoptosis': 0.0023524301833432923,
'bals r': 0.001397199827976852,
'basal': 0.0034764575410275544,
'blood': 0.010853621341137631,
'blood vessel': 0.0031260667851256397,
'bradykinin': 0.0027708076837687666,
'c-c motif chemokine 1': 0.004515416323614919,
'c-reactive protein': 0.0034587853616818063,
'cardiac failure': 0.002350378641575196,
'cardiovascular disorder': 0.00919888846066653,
'cardiovascular system': 0.009866588757093796,
'cd44 antigen': 0.004534812732391918,
'cellular secretion': 0.004739588233023713,
'cerebrovascular': 0.002327955010459226,
'chemokine': 0.004657039692111883,
'chest pain': 0.00285352889029586,
'chloroquine': 0.0017516584191543307,
'chronic disease': 0.001828074100556019,
'chronic kidney disease': 0.0024017709671377346,
'comorbidity': 0.0022953068575465477,
'confounding factors': 0.0030216706672650372,
'coronaviridae': 0.0051371282608085565,
'coronavirus': 0.018866668159786992,
'cough': 0.005549716153725856,
'covid-19': 0.05433610118159648,
'cytokine': 0.011999810473555757,
'd-dimer measurement': 0.007904179723956701,
'death': 0.01588115762541802,
'degradation': 0.003379550619191846,
'diabetes mellitus': 0.03872932193775662,
'diabetic ketoacidosis': 0.004489379965610478,
'diarrhea, ctcae': 0.00437488923081928,
'dipeptidyl peptidase 4': 0.019292255378860798,
'dna replication': 0.006114767662303313,
'dpp4i': 0.008544463701272936,
'dyspnea': 0.0030876590553554186,
'extracellular matrix': 0.0023364487459284124,
'fatigue': 0.0030876590553554186,
'fever': 0.004607872966016623,
'glucose': 0.01891629565971577,
'glucose metabolism disorder': 0.005398096884190623,
'glyburide': 0.013288960222700855,
'glycosylated hemoglobin measurement': 0.00316352693129643,
'growth factor': 0.0026633183979991887,
'h1n1': 0.002264938539929582,
'hcp': 0.0027364236231450087,
'headache': 0.0033578693582865097,
'heart': 0.009421332811370097,
'heart failure': 0.0023503786415751955,
'high sensitivity c-reactive protein measurement': 0.005099882641154376,
'hiv entry inhibitor': 0.005365135800387551,
'hmg-coa reductase inhibitor': 0.002289513092451817,
'host cell': 0.005223029773412262,
'human': 0.014092801528073864,
'human dpp4': 0.002556211710519165,
'human immunodeficiency virus': 0.0037946404784082693,
'human kidney organoids': 0.0022050307810595787,
'humoral immunity': 0.002447806997101164,
'hyperglycemia': 0.009797828654832542,
'hypertension': 0.013430293464003852,
'hypoxia': 0.0021438186717728353,
'ibuprofen': 0.0033415396684936464,
'immune cell': 0.0034992608747177354,
'immune response process': 0.0035897227204900926,
'infectious disorder': 0.01591287393608746,
'inflammation': 0.013196747867092438,
'influenza': 0.003084152937829748,
'insulin': 0.00949502983710845,
'insulin infusion': 0.001944578655114113,
'insulin resistance': 0.005983411850864118,
'interleukin': 0.0024108668083832564,
'interleukin 1 beta measurement': 0.0070970118624575345,
'interleukin-19': 0.005432616905573494,
'interleukin-6': 0.017315393375679777,
'interleukin-8': 0.00383178730610752,
'islet of langerhans': 0.002251140818756654,
'iv': 0.0012861290938934351,
'janus bifrons': 0.0012449367295877894,
'kidney': 0.008050845332539039,
'leucopenia': 0.0027088842460303865,
'leukopenia': 0.002932949994588701,
'liver': 0.004381443381638265,
'lower respiratory tract infection': 0.004531576500548021,
'lung': 0.020767410879585207,
'lymphocyte': 0.00487033347133493,
'lymphopenia': 0.005415097958458006,
'm protein': 0.0018646822018238388,
'macrophage': 0.004076946700022219,
'mellitus': 0.0010900555777919516,
'metformin': 0.004052023030357942,
'middle east respiratory syndrome': 0.006036974208200138,
'middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus': 0.013925679997029811,
'millimole per liter': 0.0021373699233968708,
'molecule': 0.002838505562387744,
'mouse': 0.011677381179374615,
'multi-organ dysfunction': 0.0029372153143388878,
'muscle': 0.002122672174800488,
'myalgia': 0.001977521539326412,
'myocardium': 0.0022345724148010787,
'neoplasm': 0.003037911877765503,
'nephropathy': 0.0019676543688425746,
'neutrophil': 0.006043543871225477,
'obesity': 0.008267711638693713,
'oral cavity': 0.0055659857338091045,
'organ': 0.002973741879099519,
'oxygen': 0.0020351103352963485,
'person': 0.004525680283686401,
'plasma': 0.0053197061181747204,
'plasmid': 0.0027226509338995376,
'pneumonia': 0.010512095493427492,
'prognosis': 0.0012386054122404233,
'proliferation': 0.006890696441541255,
'pulmonary': 0.01163903389278049,
'rbd': 0.0025247523434533924,
'receptor binding': 0.0018464368550616746,
'renal': 0.0038736869773938884,
'respiratory failure': 0.002986319777792431,
'respiratory system': 0.004329495522768546,
'sars coronavirus': 0.01735548019022084,
'sars-cov-2': 0.033049550473799,
'saxagliptin': 0.004721702323809725,
'septicemia': 0.0014192915757123858,
'serum': 0.0031395422204015004,
'serum ferritin': 0.005597172953134468,
'severe acute respiratory syndrome': 0.003097702126449046,
'shortness of breath visual analogue scale': 0.0026129361572218095,
'sitagliptin': 0.009855673950393119,
'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent': 0.003096324833939332,
'survival': 0.0035787752943805084,
't-lymphocyte': 0.005867754495528255,
'therapeutic corticosteroid': 0.0031845265341031753,
'thrombophilia': 0.004018275751713626,
'tissue': 0.0035433048999557516,
'transmembrane protein': 0.0027410790983396745,
'troponin t, cardiac muscle': 0.0029329499945887007,
'tumor necrosis factor': 0.005503860224580636,
'tzd': 0.0030216706672650372,
'vaccine': 0.003480062769988538,
'vascular': 0.009565371755902547,
'vildagliptin': 0.005452913076992331,
'viral': 0.016857758695857906,
'viral entry': 0.005437985316728421,
'viral infection': 0.005080823684964583,
'virus': 0.01628447621361242}},
'betweenness': {'distance_npmi': {'ace inhibitor': 0.00020678246484698098,
'acetaminophen': 0.0,
'acute lung injury': 0.015260545905707195,
'acute respiratory distress syndrome': 0.014640198511166254,
'adenosine': 0.009376895505927763,
'adipose tissue': 0.006782464846980976,
'angioedema': 0.006685966363385718,
'angiotensin ii receptor antagonist': 0.009015715467328371,
'angiotensin-1': 0.003143093465674111,
'angiotensin-2': 0.014006065618968845,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme': 0.0045905707196029774,
'angiotensin-converting enzyme 2': 0.0030603804797353184,
'animal': 0.006617038875103391,
'apoptosis': 0.0027564102564102567,
'bals r': 0.0,
'basal': 0.0011993382961124897,
'blood': 0.01033912324234905,
'blood vessel': 0.005872622001654259,
'bradykinin': 0.004273504273504273,
'c-c motif chemokine 1': 0.0071960297766749375,
'c-reactive protein': 0.0070168183071408876,
'cardiac failure': 0.0015536255858836503,
'cardiovascular disorder': 0.014061207609594707,
'cardiovascular system': 0.004962779156327543,
'cd44 antigen': 0.013234077750206782,
'cellular secretion': 0.01368899917287014,
'cerebrovascular': 0.0012682657843948167,
'chemokine': 0.026730079955886405,
'chest pain': 0.0059449958643507045,
'chloroquine': 0.0019713261648745518,
'chronic disease': 0.0009098428453267163,
'chronic kidney disease': 0.011248966087675765,
'comorbidity': 8.271298593879239e-05,
'confounding factors': 0.007154673283705543,
'coronaviridae': 0.010173697270471464,
'coronavirus': 0.006947890818858561,
'cough': 0.02803970223325062,
'covid-19': 0.0,
'cytokine': 0.004425144747725393,
'd-dimer measurement': 0.023738626964433417,
'death': 0.004631927212572374,
'degradation': 0.01578439481665288,
'diabetes mellitus': 0.01282051282051282,
'diabetic ketoacidosis': 0.003970223325062035,
'diarrhea, ctcae': 0.005707196029776675,
'dipeptidyl peptidase 4': 0.01108354011579818,
'dna replication': 0.010835401157981803,
'dpp4i': 0.003515301902398677,
'dyspnea': 0.002257375241246211,
'extracellular matrix': 0.007740556934105321,
'fatigue': 0.002257375241246211,
'fever': 0.004962779156327543,
'glucose': 0.007444168734491315,
'glucose metabolism disorder': 0.03432588916459884,
'glyburide': 0.0032258064516129032,
'glycosylated hemoglobin measurement': 0.01621174524400331,
'growth factor': 0.004921422663358147,
'h1n1': 0.007816377171215881,
'hcp': 0.0008271298593879239,
'headache': 0.0162979046043562,
'heart': 0.016604631927212572,
'heart failure': 0.0015536255858836503,
'high sensitivity c-reactive protein measurement': 0.013289219740832645,
'hiv entry inhibitor': 0.010794044665012407,
'hmg-coa reductase inhibitor': 0.002267714364488558,
'host cell': 0.002522746071133168,
'human': 0.004549214226633581,
'human dpp4': 0.004466501240694789,
'human immunodeficiency virus': 0.004880066170388751,
'human kidney organoids': 0.0007857733664185277,
'humoral immunity': 0.00722360077198787,
'hyperglycemia': 0.01588089330024814,
'hypertension': 0.004549214226633581,
'hypoxia': 0.0030603804797353184,
'ibuprofen': 0.020168183071408875,
'immune cell': 0.01000827129859388,
'immune response process': 0.0013234077750206782,
'infectious disorder': 0.0012406947890818859,
'inflammation': 0.0037220843672456576,
'influenza': 0.006699751861042184,
'insulin': 0.007113316790736146,
'insulin infusion': 0.004328646264130135,
'insulin resistance': 0.014185277088502896,
'interleukin': 0.002522746071133168,
'interleukin 1 beta measurement': 0.007899090157154674,
'interleukin-19': 0.022125723738626965,
'interleukin-6': 0.013316790736145575,
'interleukin-8': 0.005872622001654259,
'islet of langerhans': 0.004797353184449959,
'iv': 0.0,
'janus bifrons': 0.0,
'kidney': 0.022539288668320927,
'leucopenia': 0.01262062310449407,
'leukopenia': 0.0029914529914529912,
'liver': 0.015232974910394265,
'lower respiratory tract infection': 0.014846980976013235,
'lung': 0.004466501240694789,
'lymphocyte': 0.007954232147780536,
'lymphopenia': 0.038916459884201816,
'm protein': 0.0008684863523573201,
'macrophage': 0.008395368072787427,
'mellitus': 0.0,
'metformin': 0.004425144747725393,
'middle east respiratory syndrome': 0.005500413564929694,
'middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus': 0.005045492142266336,
'millimole per liter': 0.0016266887234629168,
'molecule': 0.01851392335263303,
'mouse': 0.008064516129032258,
'multi-organ dysfunction': 0.006792803970223326,
'muscle': 0.002564102564102564,
'myalgia': 0.0007926661152467603,
'myocardium': 0.0058519437551695615,
'neoplasm': 0.008353322304935207,
'nephropathy': 0.004962779156327543,
'neutrophil': 0.008836503997794318,
'obesity': 0.008023159636062862,
'oral cavity': 0.010752688172043012,
'organ': 0.013454645712710229,
'oxygen': 0.007154673283705542,
'person': 0.006038047973531845,
'plasma': 0.009966914805624482,
'plasmid': 0.016191066997518613,
'pneumonia': 0.012572373862696443,
'prognosis': 0.0,
'proliferation': 0.00380479735318445,
'pulmonary': 0.0347808105872622,
'rbd': 0.00380479735318445,
'receptor binding': 0.00260545905707196,
'renal': 0.012985938792390406,
'respiratory failure': 0.006406810035842295,
'respiratory system': 0.014846980976013235,
'sars coronavirus': 0.0037220843672456576,
'sars-cov-2': 0.003143093465674111,
'saxagliptin': 0.00467328370554177,
'septicemia': 0.00041356492969396195,
'serum': 0.014502343534601598,
'serum ferritin': 0.016101461262751585,
'severe acute respiratory syndrome': 0.004383788254755997,
'shortness of breath visual analogue scale': 0.00041356492969396195,
'sitagliptin': 0.006472291149710504,
'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent': 0.00641025641025641,
'survival': 0.004466501240694789,
't-lymphocyte': 0.029404466501240695,
'therapeutic corticosteroid': 0.011248966087675765,
'thrombophilia': 0.018458781362007164,
'tissue': 0.011993382961124897,
'transmembrane protein': 0.010918114143920596,
'troponin t, cardiac muscle': 0.0029914529914529912,
'tumor necrosis factor': 0.016804521643231318,
'tzd': 0.007154673283705543,
'vaccine': 0.003349875930521092,
'vascular': 0.0028949545078577337,
'vildagliptin': 0.0030603804797353184,
'viral': 0.012241521918941274,
'viral entry': 0.015508684863523574,
'viral infection': 0.006286186931348222,
'virus': 0.005789909015715467}},
'closeness': {}}
Community detection¶
Community detection methods partition the network into clusters of
densely connected nodes in a way that nodes in the same community are
more connected between themselves relatively to the nodes in different
communities. In this section we will illustrate the use of the
CommunityDetector interface provided by BlueGraph for community
detection and estimation of its quality using modularity, performance
and coverange methods. The unified interface allows us to use various
community detection methods available in different graph backends.
First, we create a NetworkX-based instance and use several different
community detection strategies provided by this library.
nx_detector = NXCommunityDetector(new_paragraph_network, directed=False)
nx_detector.graph
<networkx.classes.graph.Graph at 0x7fc6ae6035c0>
Louvain algorithm¶
partition = nx_detector.detect_communities(
strategy="louvain", weight="npmi")
print("Modularity: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="modularity", weight="npmi"))
print("Performance: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="performance", weight="npmi"))
print("Coverage: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="coverage", weight="npmi"))
Modularity: 0.34260090074583094
Performance: 0.7893189612934836
Coverage: 0.3929003630496168
Label propagation¶
partition = nx_detector.detect_communities(
strategy="lpa", weight="npmi", intermediate=False)
print("Modularity: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="modularity", weight="npmi"))
print("Performance: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="performance", weight="npmi"))
print("Coverage: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="coverage", weight="npmi"))
Modularity: 0.07719091705395371
Performance: 0.3316184876694431
Coverage: 0.9415086728519564
Stochastic block model¶
gt_detector = GTCommunityDetector(new_paragraph_network, directed=False)
partition = gt_detector.detect_communities(strategy="sbm", weight="npmi")
print("Modularity: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="modularity", weight="npmi"))
print("Performance: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="performance", weight="npmi"))
print("Coverage: ", nx_detector.evaluate_parition(partition, metric="coverage", weight="npmi"))
Modularity: 0.21771245914317255
Performance: 0.7700473624040503
Coverage: 0.2408229124647035
Writing community partition as node properties¶
nx_detector.detect_communities(
strategy="louvain", weight="npmi",
write=True, write_property="louvain_community")
new_paragraph_network = nx_detector.get_pgframe(
node_prop_types=new_paragraph_network._node_prop_types,
edge_prop_types=new_paragraph_network._edge_prop_types)
new_paragraph_network.nodes(raw_frame=True).sample(5)
| @type | paper_frequency | degree | pagerank | betweenness | louvain_community | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @id | ||||||
| multi-organ dysfunction | Entity | 2.0 | 23.0 | 0.002937 | 0.006793 | 4 |
| adenosine | Entity | 2.0 | 22.0 | 0.002692 | 0.009377 | 1 |
| millimole per liter | Entity | 2.0 | 16.0 | 0.002137 | 0.001627 | 5 |
| respiratory failure | Entity | 2.0 | 23.0 | 0.002986 | 0.006407 | 4 |
| interleukin-6 | Entity | 5.0 | 209.0 | 0.017315 | 0.013317 | 1 |
Export network and the computed metrics¶
# Save graph as JSON
new_paragraph_network.export_json("../data/literature_comention.json")
# Save the graph for Gephi import.
new_paragraph_network.export_to_gephi(
"../data/gephi_literature_comention",
node_attr_mapping = {
"degree": "Degree",
"pagerank": "PageRank",
"betweenness": "Betweenness",
"louvain_community": "Community"
},
edge_attr_mapping={
"npmi": "Weight"
})
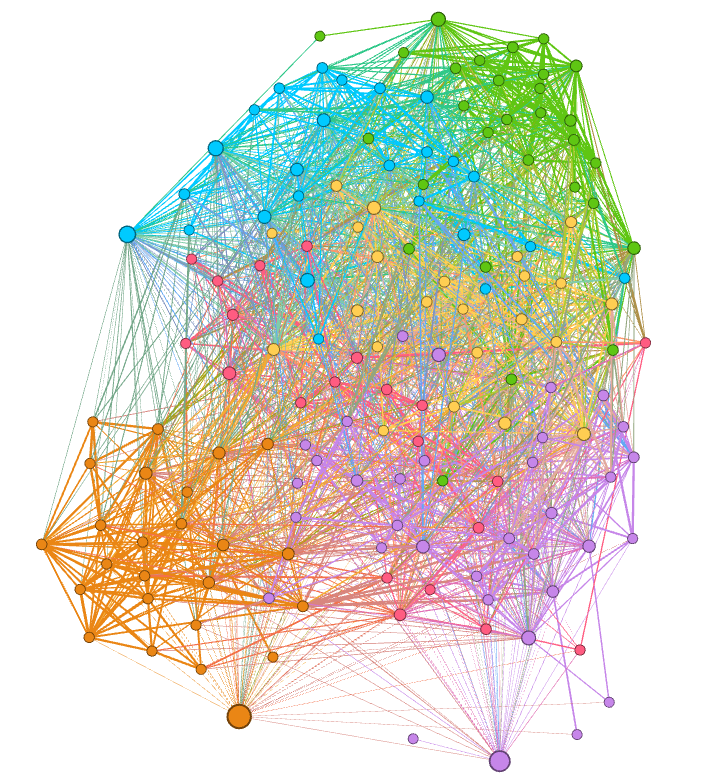
The representation of the network saved above can be imported into Gephi for producing graph visualizations, as in the following example:
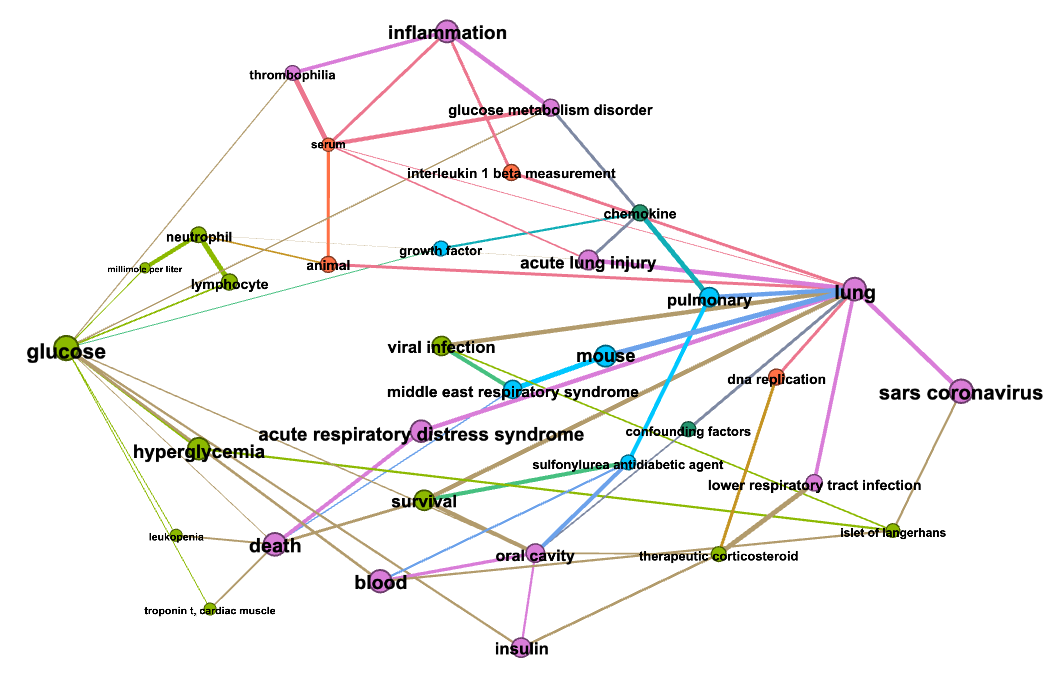
In the figures below colors represent communities detected using the Louvain algorithm (with NPMI edge weights), node sizes are proportional to the PageRank of nodes and edge thickness to the NPMI values.
Full network

Community “Symptoms and comorbidities”
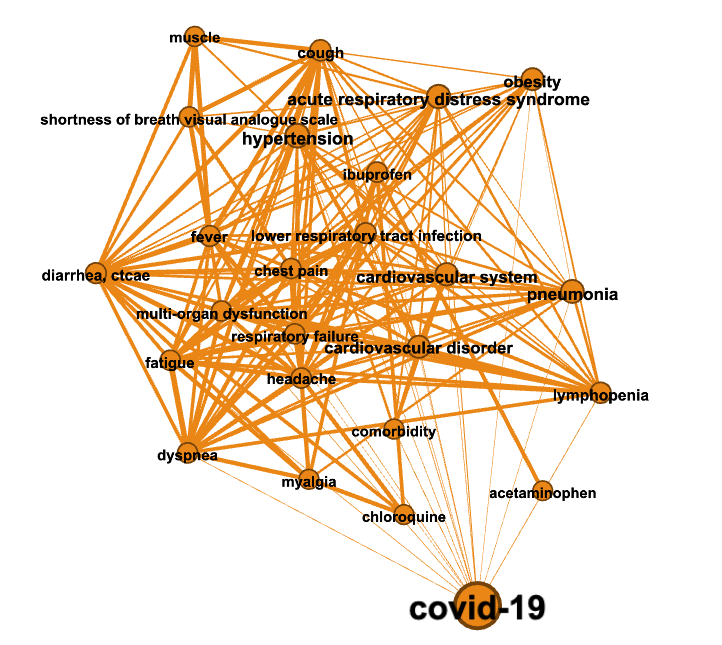
Community “Viral biology”
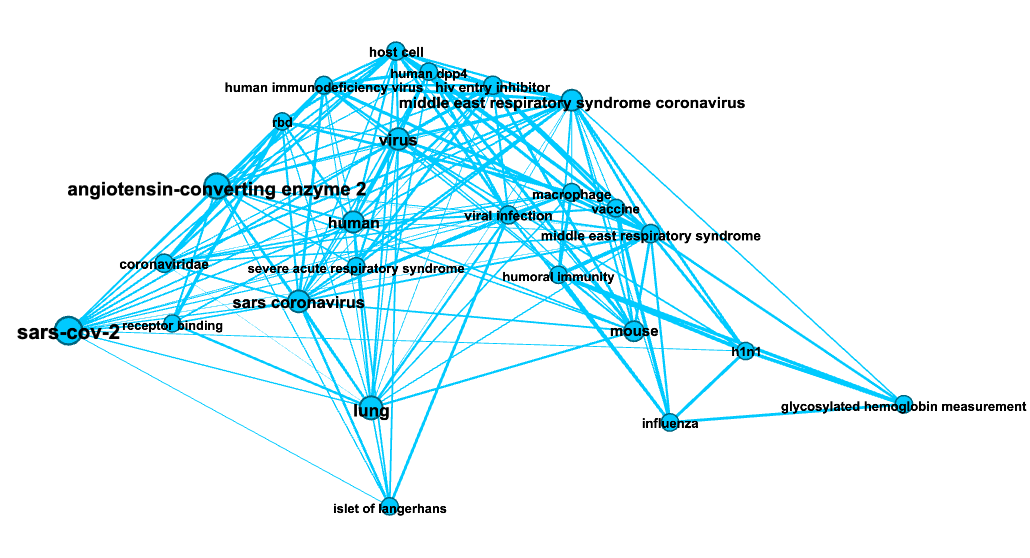
Community “Immunity”
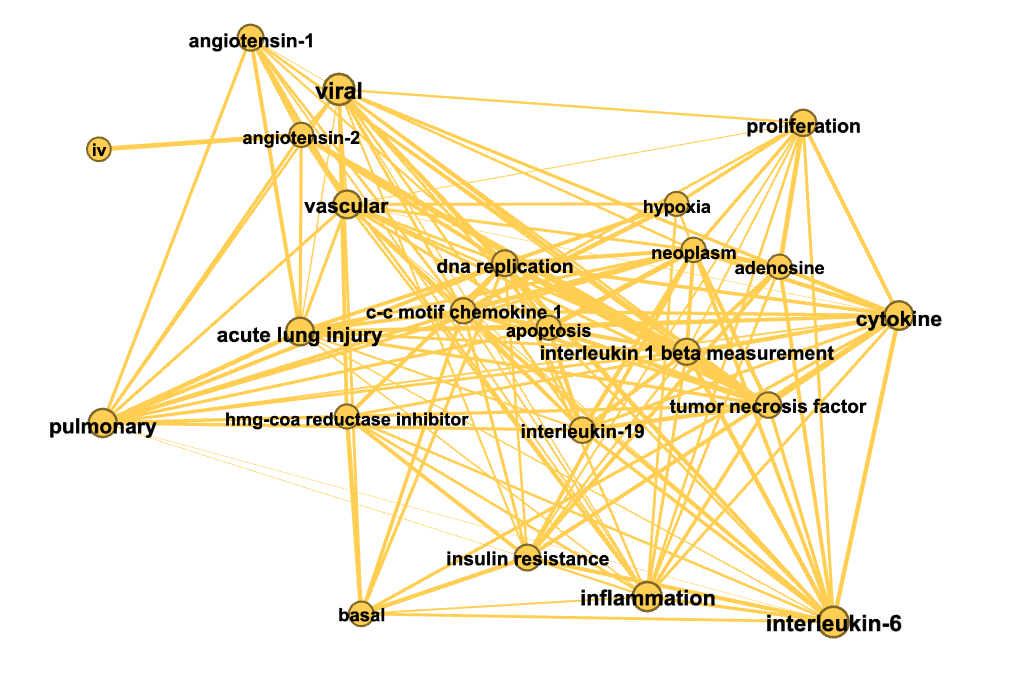
Minimum spanning trees¶
A minimum spanning tree of a network is given by a subset of edges that make the network connected (\(n - 1\) edges connecting \(n\) nodes). Its weighted version minimizes not only the number of edges included in the tree, but the total edge weight.
In the following example we compute a minimum spanning tree minimizing
the NPMI-based distance weight of the network edges. We use the
graph_tool-based implementation of the PathFinder interface.
gt_paragraph_path_finder = GTPathFinder(new_paragraph_network, directed=False)
gt_paragraph_path_finder.graph
<Graph object, undirected, with 157 vertices and 2479 edges at 0x7fc6ae3e8438>
tree = graph_tool_to_pgframe(gt_paragraph_path_finder.minimum_spanning_tree(distance="distance_npmi"))
tree.export_to_gephi(
"../data/gephi_literature_spanning_tree",
node_attr_mapping = {
"degree": "Degree",
"pagerank": "PageRank",
"betweenness": "Betweenness",
"louvain_community": "Community"
},
edge_attr_mapping={
"npmi": "Weight"
})
The representation of the network saved above can be imported into Gephi for producing graph visualizations, as in the following example:
In the figures below colors represent communities detected using the NPMI weight, node sizes are proportional to the PageRank of nodes and edge thickness to the NPMI values.
Full network
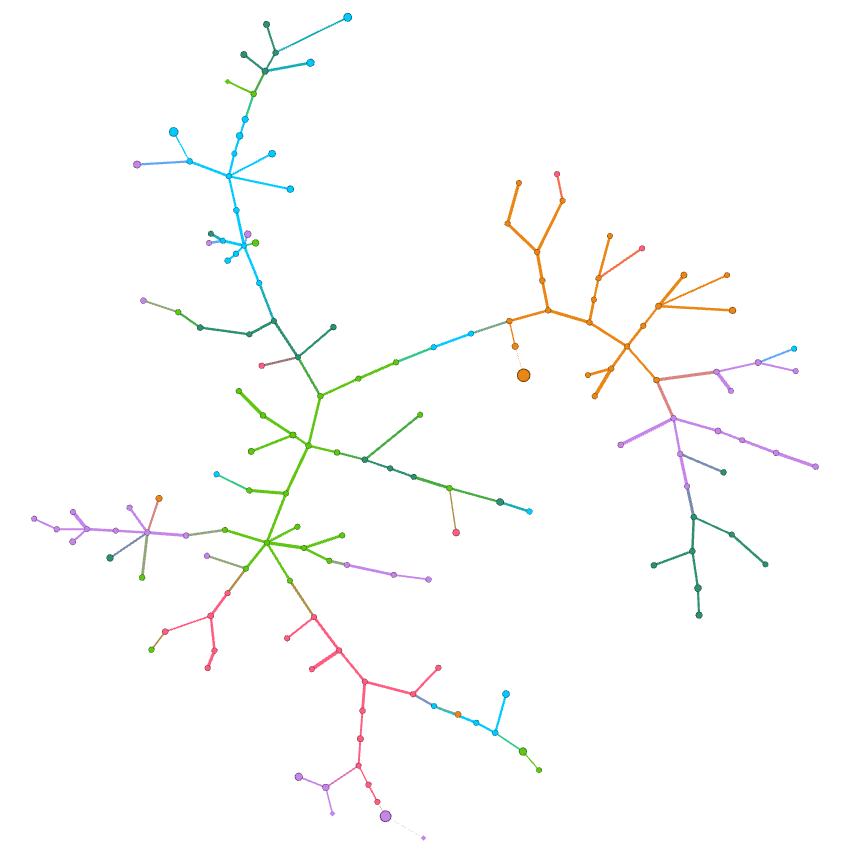
Zoom into “covid-19”
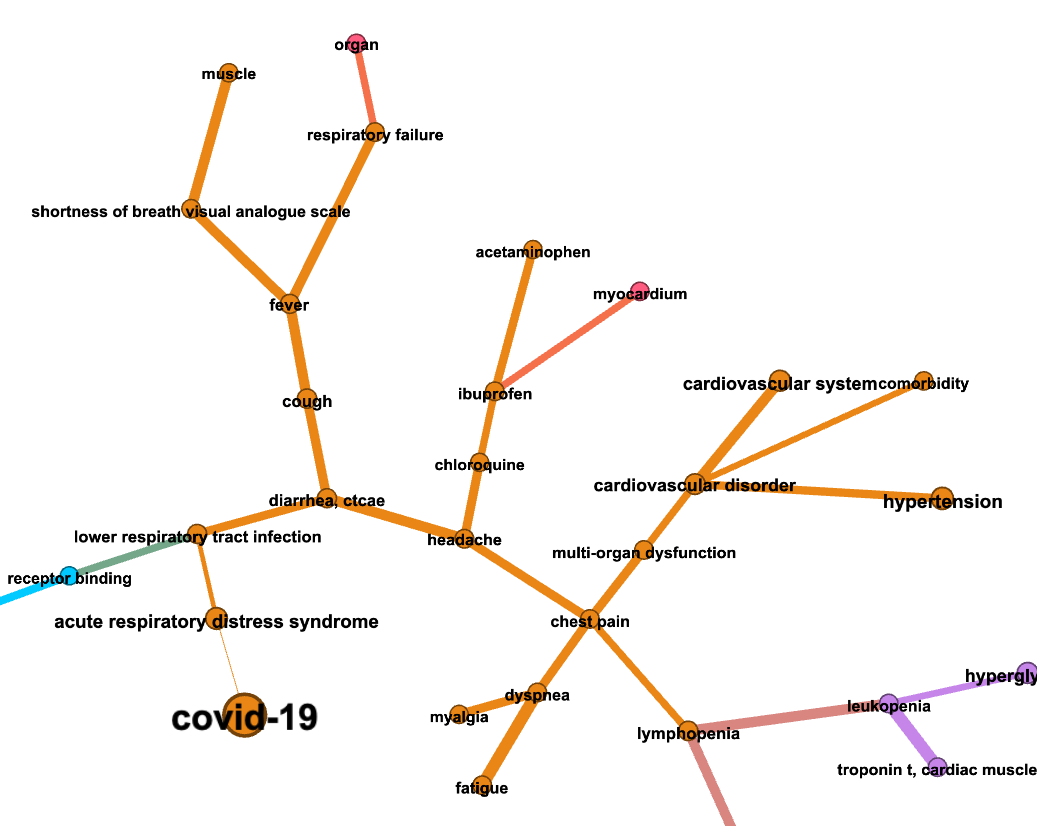
Shortest path search¶
The shortest path search problem consisits in finding a sequence of edges from the source node to the target node that minimizes the cumulative weight (or distance) associated to the edges.
path = gt_paragraph_path_finder.shortest_path("lung", "sars-cov-2")
pretty_print_paths([path])
lung <-> <-> sars-cov-2
The cell above illustrates that the single shortest path form ‘lung’ and ‘sars-cov-2’ consists of the direct edge between them.
We adapt this problem to the literature exploration task, i.e. having fixed the source and the target concepts (the relation here is actually symmetric as the edges of our network are undirected), we would like to find a set of \(n\) shortest paths between them. Moreover, we would like these paths to be indirect (not to include the direct edge from the source to the target). In the following examples we use mutual-information-based edge weights to perform our literature exploration.
The library includes two strategies for finding such \(n\) shortest paths. The first strategy uses Yen’s algorithm for finding \(n\) loopless shortest paths from the source to the target (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yen%27s_algorithm).
nx_paragraph_path_finder = NXPathFinder(new_paragraph_network, directed=False)
paths = nx_paragraph_path_finder.n_shortest_paths(
"lung", "sars-cov-2", n=10,
distance="distance_npmi", strategy="yen")
pretty_print_paths(paths)
lung <-> <-> sars-cov-2
acute lung injury
pulmonary
receptor binding
human
viral
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
host cell
dna replication
acute lung injury <-> pulmonary
The second, naive, strategy is suitable in the scenarios when our networks are large and highly dense (then the performance of Yen’s algorithm degragates as the number of edges is approaching \(O(N^2)\) with \(N\) being the number of nodes).
This strategy simply finds all the indirect shortest paths from the
source to the target (in dense graphs the most common such paths are of
length 2, i.e. source <-> intermediary <-> target, and therefore,
the number of such path is roughly proportional to the number of nodes
in the network). Then, the cumulative distance score is computed for
every path and the top \(n\) paths with the best score are selected.
paths = gt_paragraph_path_finder.n_shortest_paths(
"lung", "sars-cov-2", n=10,
distance="distance_npmi", strategy="naive")
pretty_print_paths(paths)
lung <-> <-> sars-cov-2
acute lung injury
pulmonary
receptor binding
human
viral
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
host cell
dna replication
human kidney organoids
The library provides an additional utility for finding tripaths, paths
of the shape source <-> intermediary <-> target. Setting the
parameter intersecting to False we can ensure that the entities
the sets of entities discovered on the paths source <-> intermediary
and intermediary <-> target do not overlap.
("sars-cov-2", "glucose") in new_paragraph_network.edges()
False
gt_paragraph_path_finder.n_shortest_paths(
"glucose", "sars-cov-2", n=10,
distance="distance_npmi", strategy="naive")
[('glucose', 'cerebrovascular', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'plasmid', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'basal', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'coronavirus', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'headache', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'islet of langerhans', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'serum', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'comorbidity', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'infectious disorder', 'sars-cov-2'),
('glucose', 'viral entry', 'sars-cov-2')]
path_a_b, path_b_c = gt_paragraph_path_finder.n_shortest_tripaths(
"lung", "glucose", "sars-cov-2", 10,
strategy="naive", distance="distance_npmi", overlap=False)
pretty_print_tripaths("lung", "glucose", "sars-cov-2", 10, path_a_b, path_b_c)
lung -> -> glucose -> -> sars-cov-2
inflammation cerebrovascular
islet of langerhans plasmid
serum basal
oral cavity coronavirus
death headache
middle east respiratory syndrome comorbidity
neutrophil infectious disorder
chemokine viral entry
sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent sars coronavirus
therapeutic corticosteroid person
Nested path search¶
To explore the space of co-occurring terms in depth, we can run the path search procedure presented above in a nested fashion. For each edge \(e_1, e_2, ..., e_n\) encountered on a path from the source to the target from, we can further expand it into \(n\) shortest paths between each pair of successive entities (i.e. paths between \(e_1\) and \(e_2\), \(e_2\) and \(e_3\), etc.).
paths = gt_paragraph_path_finder.n_nested_shortest_paths(
"lung", "glucose", top_level_n=10, nested_n=2, depth=2, distance="distance_npmi",
strategy="naive")
paths
[('serum', 'glucose metabolism disorder', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'lower respiratory tract infection', 'therapeutic corticosteroid'),
('inflammation', 'thrombophilia', 'glucose'),
('oral cavity', 'glucose'),
('therapeutic corticosteroid', 'insulin', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'pulmonary', 'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent'),
('oral cavity', 'blood', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'death'),
('middle east respiratory syndrome', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'therapeutic corticosteroid'),
('lung', 'neutrophil'),
('lung', 'middle east respiratory syndrome', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'serum', 'inflammation'),
('islet of langerhans', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'acute lung injury', 'neutrophil'),
('death', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'inflammation'),
('sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent', 'blood', 'glucose'),
('inflammation', 'glucose metabolism disorder', 'glucose'),
('death', 'leukopenia', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'islet of langerhans', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'survival', 'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent'),
('lung', 'neutrophil', 'glucose'),
('islet of langerhans', 'hyperglycemia', 'glucose'),
('serum', 'thrombophilia', 'glucose'),
('neutrophil', 'millimole per liter', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'islet of langerhans'),
('lung', 'death', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'serum', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'acute lung injury', 'serum'),
('chemokine', 'growth factor', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'middle east respiratory syndrome'),
('lung', 'oral cavity', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'survival', 'oral cavity'),
('lung', 'survival', 'death'),
('lung', 'mouse', 'middle east respiratory syndrome'),
('lung', 'inflammation', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'chemokine', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'acute lung injury', 'chemokine'),
('chemokine', 'glucose metabolism disorder', 'glucose'),
('sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent', 'oral cavity', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'viral infection', 'islet of langerhans'),
('lung', 'therapeutic corticosteroid', 'glucose'),
('lung', 'oral cavity'),
('lung', 'pulmonary', 'chemokine'),
('lung', 'serum'),
('middle east respiratory syndrome', 'lymphocyte', 'glucose'),
('neutrophil', 'lymphocyte', 'glucose'),
('therapeutic corticosteroid', 'oral cavity', 'glucose')]
We can now visualize the subnetwork constructed using the nodes and the edges discovered during our nested path search.
summary_graph = graph_tool_to_pgframe(
gt_paragraph_path_finder.get_subgraph_from_paths(paths))
print("Number of nodes: ", summary_graph.number_of_nodes())
print("Number of edges: ", summary_graph.number_of_edges())
Number of nodes: 27
Number of edges: 63
# Save the graph for Gephi import.
summary_graph.export_to_gephi(
"../data/gephi_literature_path_graph",
node_attr_mapping = {
"degree": "Degree",
"pagerank": "PageRank",
"betweenness": "Betweenness",
"louvain_community": "Community"
},
edge_attr_mapping={
"npmi": "Weight"
})
The resulting example graph visualized with Gephi